Have you ever struggled to find the right drill bit for your project? It can be frustrating and time-consuming.
Not all drill bits are universal. Different materials and tasks require specific types of drill bits to ensure efficiency and safety.
Keep reading to discover which drill bits are best for your needs.
Complete Guide to Drill Bits for Concrete, Metal, Tile & Wood?
Have you ever wondered why some drill bits work better on certain materials than others? Understanding the right drill bit can make your projects easier and more successful.
Drill bits are designed specifically for materials like concrete, metal, tile, and wood, each requiring unique features for optimal performance.
Let’s explore the various types and their uses in detail.

When selecting a drill bit, it’s crucial to consider the material you’re working with. For concrete, masonry bits with carbide tips are essential as they can penetrate hard surfaces. Metal drilling requires high-speed steel (HSS) bits or cobalt bits for durability and precision. Tile drilling benefits from carbide-tipped or diamond-coated bits to prevent cracking, while wood drilling is best achieved with spade bits or twist bits that provide clean and accurate holes. Each type of drill bit is engineered to handle specific challenges, ensuring efficiency and prolonging the tool’s lifespan. Additionally, using the correct bit reduces the risk of damage to both the material and the drill itself. By matching the drill bit to the material, you can achieve professional results with ease. It’s also important to maintain your drill bits by keeping them sharp and storing them properly to extend their usability.
Types of Drill Bits for Different Materials
Masonry Bits for Concrete
Masonry bits are specifically designed for drilling into hard materials like concrete1, brick, and stone. These bits typically feature carbide tips that can withstand the abrasive nature of masonry work. The carbide tip ensures that the bit remains sharp and effective even after prolonged use. When drilling into concrete, it’s important to use a hammer drill in conjunction with masonry bits to provide the necessary impact force. This combination makes the drilling process more efficient and reduces wear on the bit.
High-Speed Steel (HSS) Bits for Metal
High-Speed Steel (HSS) bits are ideal for drilling into metal due to their hardness and heat resistance. HSS bits can maintain their sharpness even when subjected to high temperatures generated during metal drilling. For tougher metals like stainless steel, cobalt HSS bits offer enhanced durability and resistance to heat, making them a preferred choice for demanding applications. These bits ensure precise and clean holes, minimizing the risk of cracking or damaging the metal.
Carbide-Tipped Bits for Tile
Drilling into tile requires precision to avoid cracking or chipping the material. Carbide-tipped bits are perfect for this task as they provide the necessary hardness to penetrate ceramic and porcelain tiles without causing damage. When using carbide-tipped bits, it’s advisable to apply water or another lubricant to keep the bit cool and reduce friction. This practice not only extends the life of the bit but also ensures a smoother drilling process.
Spade Bits for Wood
Spade bits, also known as paddle bits, are excellent for drilling large holes in wood quickly. Their flat, paddle-like shape allows for rapid material removal, making them ideal for woodworking projects that require wide openings. Spade bits are available in various sizes, enabling you to drill holes of different diameters with ease. To achieve the best results, it’s important to use a steady hand and apply consistent pressure while drilling.
Table: Comparison of Drill Bits for Various Materials
| Drill Bit Type | Best For | Key Features | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Masonry Bits | Concrete, Brick, Stone | Carbide tips, robust construction | Durable, effective on hard surfaces |
| High-Speed Steel | Metal, Stainless Steel | Heat-resistant, sharp edges | Precise, long-lasting |
| Carbide-Tipped | Tile, Ceramic | Hard carbide tips, smooth drilling | Prevents cracking, efficient cooling |
| Spade Bits | Wood | Flat paddle design, various sizes | Quick material removal, versatile sizes |
Understanding the specific requirements of each material and selecting the appropriate drill bit can significantly enhance the quality and efficiency of your projects. Proper selection not only ensures the success of your drilling tasks but also extends the lifespan of your drill bits, providing better value over time.
What are Left Handed Drill Bits?
Have you noticed drill bits that spin the opposite way? They might be left-handed drill bits.
Left-handed drill bits are designed to rotate counterclockwise, opposite to standard drill bits, offering unique benefits in specific applications.
Discover how they can be useful in your toolbox.

Left-handed drill bits are engineered to rotate in the opposite direction of conventional bits. This design can be particularly useful when trying to remove broken screws or bolts, as the reverse rotation can help unscrew them. Additionally, left-handed bits can reduce the risk of stripping screws by providing better control and torque. They are also beneficial in preventing the drill from getting stuck, as the reverse motion helps in smoother operation. However, it’s important to note that left-handed drill bits may not be suitable for all materials and tasks. They are typically used in combination with standard bits to provide versatility in your drilling operations. Understanding when and how to use left-handed drill bits can enhance your efficiency and effectiveness in various DIY and professional projects.
How Left-Handed Drill Bits Enhance Your Toolbox
Left-handed drill bits2 are a valuable addition to any toolkit, especially for those who frequently encounter stuck or stripped screws. The reverse rotation helps in loosening screws that standard bits cannot, making them indispensable for repairs and maintenance tasks. For example, if a screw becomes stuck due to rust or over-tightening, a left-handed drill bit can apply counter-torque to release it without damaging the surrounding material.
Benefits of Using Left-Handed Drill Bits
-
Enhanced Control and Torque
- The reverse rotation allows for greater control when dealing with stubborn screws.
- Reduces the likelihood of over-tightening, which can strip screws or damage materials.
-
Prevents Drill Binding
- The opposite spinning direction minimizes the chance of the drill getting stuck in the material.
- Ensures smoother operation, especially when working with dense or resistant materials.
-
Versatility in Applications
- Useful in both professional and DIY projects where screw removal is common.
- Can be used alongside standard drill bits for a more comprehensive toolkit.
When to Use Left-Handed Drill Bits
- Removing Broken Screws: Ideal for extracting screws that are too damaged to be removed with standard bits.
- Preventing Stripping: Helps in maintaining the integrity of screws during removal and installation.
- Specialized Tasks: Beneficial in applications requiring precise control and reduced torque.
Table: Comparison Between Standard and Left-Handed Drill Bits
| Feature | Standard Drill Bits | Left-Handed Drill Bits |
|---|---|---|
| Rotation Direction | Clockwise | Counterclockwise |
| Primary Use | Drilling and screwing in | Removing stuck or stripped screws |
| Control and Torque | Higher tendency to strip screws | Enhanced control, reduced stripping |
| Drill Binding Risk | Higher in dense materials | Lower due to reverse motion |
| Versatility | Broad range of applications | Specialized for screw removal |
Incorporating left-handed drill bits into your toolkit not only provides additional functionality but also equips you with the right tools to handle a wider range of drilling and screw removal tasks efficiently. Their unique design complements standard drill bits, ensuring that you are prepared for any challenge that may arise during your projects.
Do Left-Handed Drill Bits Work?
Have you tried using left-handed drill bits and wondered if they actually work? You’re not alone.
Left-handed drill bits do work effectively for specific tasks like removing stuck screws and bolts, providing a practical solution in challenging situations.
Learn more about their effectiveness and applications.

Left-handed drill bits are effective in several scenarios, particularly when dealing with stuck or stripped screws. The reverse rotation can help loosen and remove screws that standard bits struggle with. They are also useful in reducing the likelihood of drill binding, which can occur when a standard bit gets stuck in the material. Additionally, left-handed bits can enhance control and torque, making them ideal for delicate tasks that require precision. However, their effectiveness can vary depending on the material and the specific application. It’s important to use them in conjunction with other tools and techniques to achieve the best results. While they may not replace standard drill bits entirely, left-handed drill bits are a valuable addition to any toolkit, offering unique advantages in certain situations.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Left-Handed Drill Bits
The effectiveness of left-handed drill bits3 is largely dependent on the context in which they are used. When faced with stubborn screws or bolts, these bits can provide the necessary reverse torque to free the fasteners without causing further damage. Their design allows for better grip and control, which is essential in preventing the drill from slipping or stripping the screw head.
Practical Applications of Left-Handed Drill Bits
-
Automotive Repairs
- Removing stubborn bolts and screws in tight spaces.
- Ideal for tasks like brake pad replacement or engine maintenance.
-
Construction and Carpentry
- Extracting nails or screws that are deeply embedded in wood or other materials.
- Useful for demolition tasks where fasteners need to be removed efficiently.
-
Household Repairs
- Fixing furniture or fixtures where screws are difficult to reach or have been overtightened.
- Enhances the ease of DIY projects by providing reliable screw removal.
User Experiences and Feedback
Many users have reported significant improvements in their ability to remove difficult screws after incorporating left-handed drill bits into their toolkits. The reverse rotation feature not only saves time but also reduces the frustration associated with stuck fasteners. Additionally, professionals appreciate the added control and precision these bits offer, especially in tasks that require delicate handling.
Tips for Maximizing the Use of Left-Handed Drill Bits
To ensure that left-handed drill bits work effectively, consider the following tips:
- Use the Right Drill Speed: Adjust the drill speed to match the task. Higher speeds may be necessary for softer materials, while lower speeds are better for harder materials.
- Apply Consistent Pressure: Maintain steady pressure while drilling to prevent the bit from slipping or stripping the screw.
- Combine with Other Tools: Use left-handed bits in conjunction with screw extractors or other removal tools for enhanced effectiveness.
- Maintain Your Bits: Keep the drill bits sharp and free from debris to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Table: Common Scenarios and Left-Handed Drill Bit Effectiveness
| Scenario | Effectiveness of Left-Handed Bits | Additional Tools Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Removing Rusted Screws | High | Screw extractor |
| Extracting Stripped Bolts | Moderate to High | Pliers or vice grips |
| Tightening Reverse Threads | Low | Standard bits may be better |
| Drilling into Dense Materials | Moderate | Hammer drill for masonry tasks |
By understanding the specific scenarios where left-handed drill bits excel, you can better integrate them into your toolkit and utilize them to their full potential. Their unique functionality provides practical solutions to common drilling challenges, enhancing both efficiency and effectiveness in your projects.
What Is the Difference Between HCS and HSS Drill Bits?
Confused about HCS and HSS drill bits? You’re not alone.
HCS (High Carbon Steel) and HSS (High-Speed Steel) drill bits differ in material composition and performance, impacting their suitability for various tasks.
Let’s break down their differences and uses.

HCS drill bits are made from high carbon steel, which makes them suitable for drilling into softer materials like wood and plastic. They are generally more affordable but lack the durability and heat resistance of HSS bits. On the other hand, HSS drill bits are crafted from high-speed steel, which contains elements like tungsten, molybdenum, and chromium. This composition provides superior hardness, heat resistance, and durability, making HSS bits ideal for drilling into harder materials such as metal and masonry. Additionally, HSS drill bits can withstand higher temperatures without losing their temper, ensuring longer tool life and consistent performance. While HCS bits may be sufficient for light-duty tasks, investing in HSS drill bits is beneficial for more demanding applications, offering greater versatility and reliability in various drilling scenarios.
Understanding the Composition and Performance
The primary difference between HCS4 and HSS drill bits lies in their material composition, which directly affects their performance and application suitability.
High Carbon Steel (HCS) Drill Bits
HCS drill bits are made from high carbon steel, which provides good hardness and strength for drilling into softer materials. The high carbon content increases the steel’s hardness, making these bits effective for wood, plastic, and other non-metallic materials. However, HCS bits are more prone to wear and dulling when used on harder materials like metal or masonry. They are also less resistant to heat, which can limit their performance in high-temperature drilling scenarios.
High-Speed Steel (HSS) Drill Bits
HSS drill bits are manufactured from high-speed steel, an alloy that includes elements such as tungsten, molybdenum, and chromium. These additions enhance the steel’s hardness, heat resistance, and durability, making HSS bits suitable for a wider range of materials, including metal, stainless steel, and masonry. HSS drill bits maintain their hardness even at elevated temperatures, allowing for prolonged use without significant wear. This makes them a preferred choice for both professional and heavy-duty drilling tasks.
Comparative Performance Analysis
| Feature | HCS Drill Bits | HSS Drill Bits |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High Carbon Steel | High-Speed Steel (with tungsten, molybdenum, chromium) |
| Best For | Wood, Plastic, Soft Materials | Metal, Stainless Steel, Masonry |
| Heat Resistance | Low | High |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Generally cheaper | Typically more expensive |
| Longevity | Shorter lifespan in demanding tasks | Longer lifespan, especially in hard materials |
| Maintenance | Requires more frequent sharpening | Retains sharpness longer |
Practical Applications
Understanding the differences between HCS and HSS drill bits can help you choose the right bit for your specific needs. For instance, if you’re primarily working with wood or plastic, HCS bits are a cost-effective choice that provides sufficient performance. However, if your projects involve metal or require higher precision and durability, HSS bits are the better option despite their higher cost.
When to Choose HCS Drill Bits
- DIY Woodworking Projects: Ideal for creating clean and precise holes in wooden materials.
- Plastics and Soft Materials: Effective for drilling into plastic sheets or other soft substances without causing damage.
- Budget-Friendly Tasks: Suitable for occasional use where high durability is not a primary concern.
When to Opt for HSS Drill Bits
- Metalworking: Essential for drilling into steel, aluminum, and other metals with ease and precision.
- Professional Construction: Provides reliability and longevity for heavy-duty drilling tasks in construction projects.
- High-Temperature Applications: Maintains hardness and performance even when subjected to high temperatures during drilling.
Table: HCS vs. HSS Drill Bits in Various Scenarios
| Scenario | HCS Drill Bits | HSS Drill Bits |
|---|---|---|
| Drilling into Soft Wood | Excellent | Good |
| Drilling into Hardwood | Good | Excellent |
| Drilling into Aluminum | Fair | Excellent |
| Drilling into Stainless Steel | Poor | Excellent |
| Drilling into Masonry | Poor | Good |
| General DIY Projects | Good | Good |
| Professional Metalworking | Fair | Excellent |
By carefully considering the material you will be drilling into and the specific requirements of your project, you can make an informed decision between HCS and HSS drill bits. Investing in the right type of drill bit not only improves the quality of your work but also enhances the efficiency and longevity of your tools.
What are the Cutting Constants of High Speed Steel (HSS)?
Ever wondered what makes High Speed Steel (HSS) drill bits so effective? Let’s dive into their cutting constants.
High Speed Steel (HSS) drill bits have superior cutting constants, including hardness, heat resistance, and durability, making them ideal for a wide range of drilling tasks.
Understand the factors that contribute to their performance.
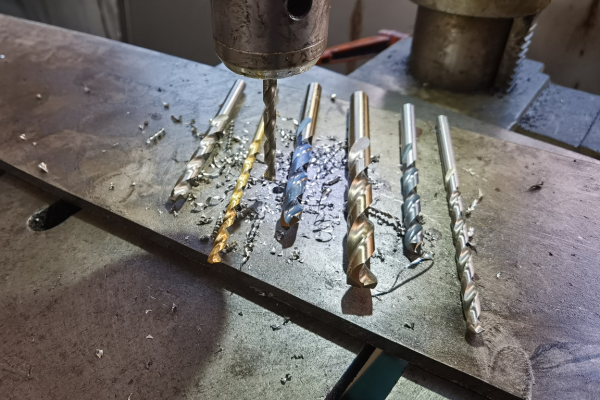

High Speed Steel (HSS) drill bits are renowned for their exceptional cutting constants, which include hardness, heat resistance, and toughness. The hardness of HSS allows the drill bits to maintain a sharp edge, ensuring efficient cutting through tough materials without dulling quickly. Heat resistance is another critical factor, as HSS can withstand high temperatures generated during drilling, preventing loss of temper and maintaining structural integrity. This property is particularly important when drilling into hard metals and other challenging materials that generate significant friction and heat. Additionally, the durability of HSS drill bits means they have a longer lifespan compared to other types, reducing the need for frequent replacements and providing better value over time. These cutting constants make HSS drill bits a preferred choice for both professional and DIY projects, offering reliable performance and versatility across various applications.
Exploring the Cutting Constants of HSS Drill Bits
The cutting performance of High Speed Steel (HSS) drill bits5 is determined by several key factors. Understanding these can help you appreciate why HSS bits are favored in many drilling applications.
Hardness
HSS drill bits are significantly harder than their counterparts, such as High Carbon Steel (HCS) bits. This hardness allows them to maintain a sharp cutting edge even when drilling through tough materials like metal and masonry. The hardness of HSS is achieved through the addition of alloying elements like tungsten, molybdenum, and chromium, which enhance the steel’s overall strength and durability.
Heat Resistance
One of the standout features of HSS drill bits is their ability to resist heat buildup during drilling. High temperatures can cause drill bits to lose their temper, leading to a reduction in hardness and, consequently, a dulling of the cutting edge. HSS drill bits are designed to withstand these temperatures without significant degradation, ensuring consistent performance even during prolonged use.
Toughness
Toughness refers to a material’s ability to absorb energy and resist fracture. HSS drill bits possess excellent toughness, allowing them to handle the stresses of drilling without breaking or chipping. This property is particularly important when drilling into hard or abrasive materials, where the risk of bit failure is higher.
Enhancing Performance with HSS Drill Bits
To maximize the performance of HSS drill bits, consider the following practices:
- Proper Drilling Technique: Use steady, controlled pressure to prevent excessive heat buildup and ensure a clean cut.
- Lubrication: Apply cutting fluids or lubricants when drilling into metals to reduce friction and heat generation.
- Bit Maintenance: Keep HSS bits sharp by regularly honing or sharpening them to maintain their cutting efficiency.
- Appropriate Drill Speed: Adjust the drill speed based on the material being drilled. Higher speeds are suitable for softer materials, while lower speeds are better for harder substances.
Table: Performance Attributes of HSS Drill Bits
| Cutting Constant | Description | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | High resistance to deformation and wear | Maintains sharp cutting edge, drills efficiently through tough materials |
| Heat Resistance | Ability to withstand high temperatures without losing temper | Prevents dulling, ensures consistent performance under heavy use |
| Toughness | Capacity to absorb energy and resist fracture | Reduces risk of bit breakage or chipping during drilling |
Practical Applications Leveraging HSS Cutting Constants
The superior cutting constants of HSS drill bits make them suitable for a wide range of applications:
- Metalworking: HSS bits are ideal for drilling into various metals, including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, thanks to their hardness and heat resistance.
- Construction: Whether drilling into masonry or concrete, HSS drill bits provide the necessary durability and performance for demanding construction tasks.
- Automotive Repairs: HSS bits can handle the tough materials found in automotive applications, such as engine components and metal panels.
- General DIY Projects: From woodworking to plumbing, HSS drill bits offer the versatility needed for diverse DIY tasks, ensuring reliable and efficient drilling.
By understanding and leveraging the cutting constants of HSS drill bits, you can achieve superior drilling performance across a variety of materials and applications. Their combination of hardness, heat resistance, and toughness ensures that HSS bits remain a staple in both professional toolkits and home DIY arsenals.
What Is the Difference Between SDS and HSS Drill Bits?
Not sure when to use SDS versus HSS drill bits? Let’s clarify their differences.
SDS (Slotted Drive System) and HSS (High-Speed Steel) drill bits serve different purposes, with SDS being ideal for heavy-duty masonry work and HSS suitable for a variety of materials including metal and wood.
Find out which one you need for your project.
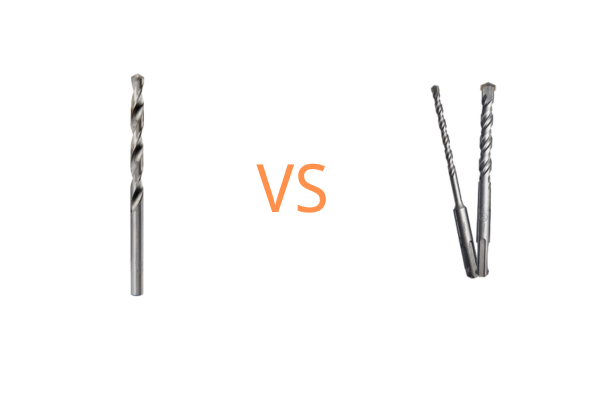

SDS (Slotted Drive System) and HSS (High-Speed Steel) drill bits are designed for distinct applications. SDS drill bits are specifically engineered for heavy-duty masonry work, such as drilling into concrete, brick, and stone. They feature a unique shank design that allows for quick and secure bit changes in SDS-compatible hammer drills, providing better power transfer and reduced bit slippage during intense drilling tasks. This makes SDS bits ideal for construction and large-scale projects that require robust and reliable performance. In contrast, HSS drill bits are versatile and suitable for a wide range of materials, including metal, wood, and plastic. Their high-speed steel construction offers excellent durability, heat resistance, and precision, making them a staple in both professional and DIY toolkits. While SDS bits excel in masonry applications, HSS bits provide the flexibility needed for various drilling tasks, ensuring that you have the right tool for any job.
Comparing SDS and HSS Drill Bits
Understanding the key differences between SDS and HSS drill bits can help you choose the right bit for your specific drilling needs.
SDS Drill Bits
SDS drill bits are designed for use with hammer drills, which combine rotary motion with a hammering action to efficiently drill into hard materials like concrete and masonry6. The SDS shank has grooves that fit into the chuck of an SDS drill, allowing for quick and tool-free bit changes. This design not only enhances the stability of the bit during drilling but also improves the transfer of energy from the drill to the bit, resulting in faster and more efficient drilling.
Key Features of SDS Drill Bits:
- Shank Design: Slotted for secure fitting in SDS-compatible hammer drills.
- Durability: Built to withstand the high-impact forces of hammer drilling.
- Efficiency: Optimized for rapid drilling into masonry and concrete.
HSS Drill Bits
HSS drill bits are more versatile and can be used with standard rotary drills for a variety of materials. Their high-speed steel composition allows them to maintain sharpness and precision, making them suitable for drilling into metals, wood, and plastic. Unlike SDS bits, HSS bits do not have a specialized shank and are instead designed to fit into standard drill chucks. This makes them more adaptable for different drilling tasks but less effective for heavy-duty masonry work compared to SDS bits.
Key Features of HSS Drill Bits:
- Material: Made from high-speed steel for versatility and durability.
- Shank Design: Standard shank suitable for a wide range of drills.
- Versatility: Effective for drilling into metal, wood, plastic, and other materials.
Practical Applications
Choosing between SDS and HSS drill bits depends largely on the nature of your project and the materials you are working with.
When to Use SDS Drill Bits
- Concrete Drilling: Ideal for installing anchors, rebar, and other fixtures in concrete structures.
- Masonry Work: Perfect for tasks like drilling into brick walls, stone surfaces, and other masonry materials.
- Construction Projects: Essential for large-scale construction tasks that require efficient and powerful drilling capabilities.
When to Use HSS Drill Bits
- Metalworking: Suitable for drilling into various metals, including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel.
- Woodworking: Ideal for creating precise and clean holes in wooden materials.
- General DIY: Versatile enough for a wide range of home improvement and repair tasks.
Table: SDS vs. HSS Drill Bits Comparison
| Feature | SDS Drill Bits | HSS Drill Bits |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Concrete, Brick, Masonry | Metal, Wood, Plastic |
| Shank Design | Slotted for SDS-compatible drills | Standard shank for rotary drills |
| Drill Compatibility | SDS hammer drills | Standard rotary drills |
| Durability | High for heavy-duty applications | High for versatile applications |
| Efficiency | Superior in masonry drilling | Excellent for precision drilling |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized use | Varies, generally affordable |
Combining SDS and HSS Drill Bits in Your Toolkit
Having both SDS and HSS drill bits in your toolkit ensures that you are prepared for a wide range of drilling tasks. SDS bits handle the heavy-duty masonry work, while HSS bits take care of more delicate and versatile drilling needs. This combination provides comprehensive coverage for most construction, DIY, and professional projects, allowing you to switch between different types of drilling with ease.
Tips for Using SDS and HSS Drill Bits Effectively
- Match the Bit to the Task: Always choose the drill bit that is best suited for the material and type of drilling you are performing.
- Maintain Your Bits: Keep both SDS and HSS bits clean and sharp to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Use the Right Drill: Ensure that you are using an SDS-compatible hammer drill for SDS bits and a standard rotary drill for HSS bits to maximize efficiency.
- Proper Storage: Store your drill bits in a dry, organized place to prevent damage and prolong their lifespan.
By understanding the distinct features and applications of SDS and HSS drill bits, you can enhance your drilling efficiency and achieve better results across a variety of projects. Selecting the right drill bit for the job not only improves the quality of your work but also extends the life of your tools, providing greater value and reliability in your drilling tasks.
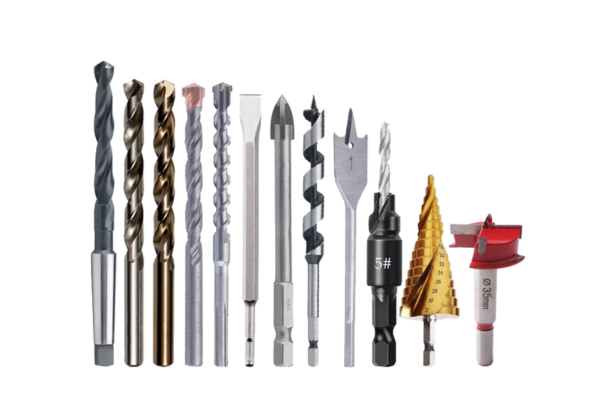
How Many Types of Drill Bits?
Are you overwhelmed by the variety of drill bits available? You’re not alone.
There are numerous types of drill bits, each designed for specific materials and tasks, including twist bits, spade bits, masonry bits, and more.
Explore the different types and their uses.

Drill bits come in a wide array of types, each tailored to specific materials and applications. The most common types include:
Twist Bits
Twist bits are the most widely used drill bits, suitable for drilling into wood, metal, and plastic. Their spiral design7 helps remove debris efficiently.
Spade Bits
Spade bits, also known as paddle bits, are ideal for drilling large holes in wood. They have a flat, paddle-like shape that allows for quick material removal.
Masonry Bits
Masonry bits are designed for drilling into hard materials like concrete, brick, and stone. They typically feature carbide tips to withstand the abrasiveness of these surfaces.
Brad Point Bits
Brad point bits are perfect for woodworking projects, providing precise and clean holes with minimal splintering.
Hole Saws
Hole saws are used for cutting large-diameter holes in wood, metal, and plastic. They consist of a cylindrical saw with serrated edges that rotate to cut through the material.
Forstner Bits
Forstner bits are specialized for drilling flat-bottomed holes in wood, offering high precision and smooth finishes.
Step Bits
Step bits are conical drill bits used for drilling multiple hole sizes in thin materials like sheet metal and plastic. Their stepped design allows for versatility in hole diameters.
Auger Bits
Auger bits are designed for deep drilling in wood, featuring a screw tip that helps pull the bit through the material.
Holemaker Bits
Holemaker bits are designed for fast and efficient hole-making in wood and other soft materials. They often feature a unique design that allows for rapid drilling with minimal effort.
Masonry Bits
Masonry bits are essential for drilling into hard materials such as concrete, brick, and stone. They usually have carbide tips that provide the necessary hardness and durability to penetrate these tough surfaces without dulling quickly.
Cobalt Bits
Cobalt bits are a type of HSS bit that contains cobalt, making them exceptionally hard and resistant to heat. They are ideal for drilling into very hard metals, such as stainless steel, without losing their edge.
Titanium-Coated Bits
Titanium-coated bits offer increased durability and resistance to corrosion. The titanium coating reduces friction, allowing the bit to stay cooler and last longer during use.
Glass and Tile Bits
These bits are specifically designed for drilling into glass and ceramic tiles. They usually have a spear-point tip that helps to prevent cracking and chipping of the material.
Diamond Bits
Diamond bits are the most durable and effective for drilling into extremely hard materials like glass, stone, and certain types of masonry. They feature diamond-coated tips that provide superior cutting power.
Countersink Bits
Countersink bits are used to create a conical hole that allows screw heads to sit flush with or below the surface of the material. This is particularly useful in woodworking and metalworking to ensure a smooth finish.
Brad Point Bits
Brad point bits are excellent for precision drilling in wood. They have a sharp point that helps to keep the bit in place, preventing it from wandering and ensuring accurate hole placement.
Flute Types
The flute design of a drill bit plays a crucial role in its performance. The flutes are the spiral grooves that run along the length of the bit, helping to remove debris from the hole being drilled. Different flute designs are optimized for different materials and drilling speeds.
Specialized Bits
There are also numerous specialized drill bits designed for specific tasks, such as tiling, plumbing, and electrical work. These bits often incorporate unique features tailored to their intended applications, providing enhanced performance and ease of use.
Table: Overview of Common Drill Bit Types
| Drill Bit Type | Best For | Key Features | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Twist Bits | Wood, Metal, Plastic | Spiral design, versatile | Efficient debris removal, widely available |
| Spade Bits | Wood | Flat paddle shape, large diameter | Quick material removal, easy to use |
| Masonry Bits | Concrete, Brick, Stone | Carbide tips, robust construction | Durable, effective on hard surfaces |
| Brad Point Bits | Wood | Sharp point, precise drilling | Clean holes, minimal splintering |
| Hole Saws | Large-diameter holes | Cylindrical saw with serrated edges | Versatile, cuts large holes efficiently |
| Forstner Bits | Wood | Flat-bottomed design, high precision | Smooth finishes, precise hole placement |
| Step Bits | Thin materials | Conical shape, multiple drilling steps | Versatile hole sizes, efficient drilling |
| Auger Bits | Deep drilling in wood | Screw tip, long shank | Pulls bit through material, deep holes |
| Cobalt Bits | Hard metals | High-speed steel with cobalt | Exceptional hardness, heat resistance |
| Titanium-Coated Bits | Various materials | Titanium coating for durability | Reduced friction, extended lifespan |
| Glass and Tile Bits | Glass, Ceramic tiles | Spear-point tip, precision drilling | Prevents cracking, clean hole edges |
| Diamond Bits | Extremely hard materials | Diamond-coated tips | Superior cutting power, high durability |
| Countersink Bits | Wood, Metal | Conical shape for flush screw heads | Smooth finishes, professional look |
Choosing the Right Drill Bit for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate drill bit type is essential for achieving the best results in your projects. Consider the following factors when choosing a drill bit:
- Material: Determine the material you will be drilling into, as different bits are optimized for specific materials.
- Hole Size: Select a bit that matches the desired hole diameter, especially for tasks requiring precise sizing.
- Depth of Hole: For deep drilling tasks, such as installing long screws or bolts, choose bits designed for extended reach, like auger bits.
- Drill Type: Ensure that the bit is compatible with your drill, whether it’s a standard rotary drill or a specialized hammer drill for masonry work.
- Precision Requirements: For projects requiring high precision and clean holes, such as woodworking or metalworking, opt for bits like brad point or Forstner bits.
- Frequency of Use: Consider the durability and longevity of the bit, especially if it will be used frequently or in demanding applications.
Table: Drill Bit Selection Guide
| Factor | Consideration | Recommended Drill Bit Types |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Type of material being drilled | HSS, Masonry, Diamond, Cobalt |
| Hole Size | Desired diameter of the hole | Twist, Spade, Hole Saws, Step Bits |
| Depth of Hole | How deep the hole needs to be | Auger, Forstner |
| Drill Type | Type of drill being used | SDS for masonry, standard for HSS |
| Precision | Level of precision required | Brad Point, Forstner |
| Frequency of Use | How often the bit will be used | Durable options like HSS, Cobalt |
By carefully considering these factors and understanding the unique features of each drill bit type, you can ensure that you select the most appropriate bit for your specific drilling needs. This not only enhances the quality of your work but also improves efficiency and prolongs the lifespan of your drill bits.
Conclusion
Choosing the right drill bit makes all the difference in your projects.

Selecting the appropriate drill bit is crucial for achieving efficient and high-quality results in any drilling project. By understanding the various types of drill bits and their specific applications, you can ensure that you are well-equipped to handle a wide range of materials and tasks. Whether you are working with wood, metal, masonry, or other materials, using the right drill bit enhances the precision and durability of your work, reduces frustration, and extends the life of your tools. Invest time in selecting and maintaining the proper drill bits, and you’ll find that your projects become smoother, faster, and more successful.
-
refers to a fundamental material in masonry. ↩
-
refers to the core topic of the paragraph. ↩
-
are a specialized tool, so it’s important to link to a detailed resource that explains what they are and how they work. ↩
-
are commonly used in specific applications, and adding a link to a reputable resource would help readers understand the advantages, disadvantages, and proper uses of HCS drill bits. ↩
-
is a critical material used in drilling, and understanding its performance factors is essential for professionals choosing the right drill bits. ↩
-
another common material for SDS drills. ↩
-
crucial for debris removal. ↩